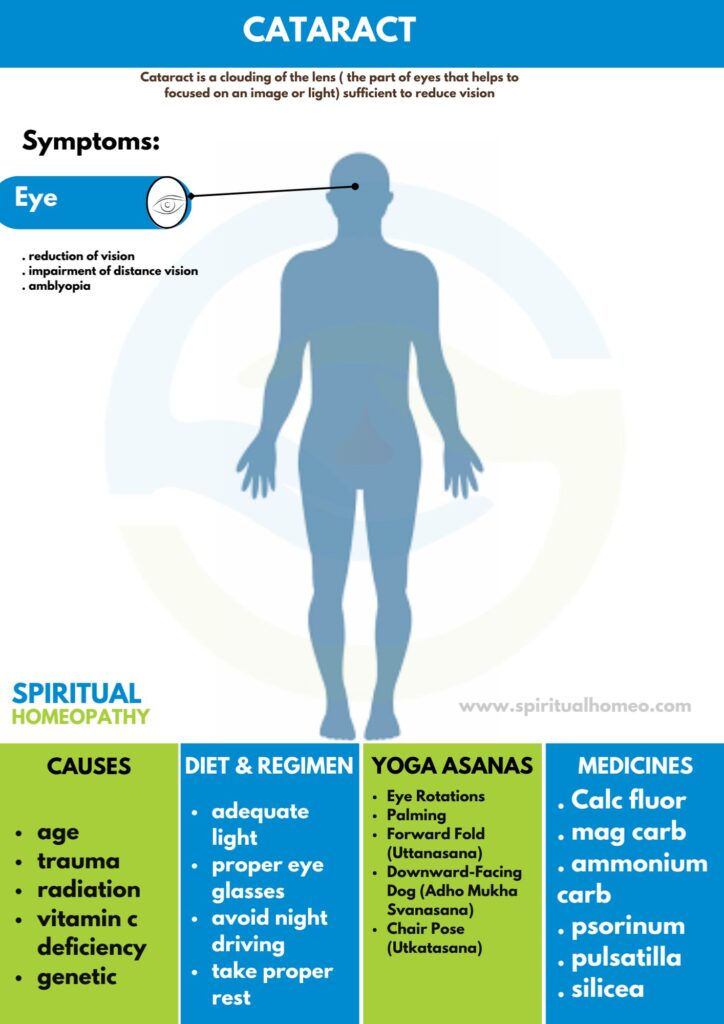
What Causes Cataracts?
Cataracts develop for several reasons, with age being the most common factor. However, multiple environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors can also contribute to the condition. Here’s an overview of the key causes of cataracts:
1. Age-Related Changes
The natural aging process is the most frequent cause of cataracts. As we age, the proteins in the eye’s lens begin to break down and degrade. This process accelerates in individuals with conditions like diabetes or hypertension, leading to clouding of the lens and impaired vision over time.
2. Environmental Factors
Radiation: Exposure to ionizing radiation like X-rays can damage the DNA of the lens cells, increasing the risk of cataracts. Ultraviolet (UVB) light from the sun is another major cause, as long-term UV exposure can harm the lens, leading to cataract formation. Wearing sunglasses from an early age can help slow the development of cataracts later in life.
Toxins: Environmental toxins, including smoking and pollution, can also contribute to the development of cataracts.
3. Trauma
Injuries to the eye, such as blunt trauma or penetrating eye injuries, can damage the lens capsule and cause cataracts. In some cases, trauma may lead to star-shaped or petal-shaped cataracts. Electric burns or electrical injuries are another cause, with cataracts occurring in 0.7% to 8% of such cases.
4. Genetics
Genetic factors play a significant role in cataract development. Inherited conditions may cause cataracts to develop early in life or in childhood. Certain genetic syndromes, like atopic dermatitis or eczema, may also increase the risk of cataracts, particularly shield ulcer cataracts.
5. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Cigarette smoking doubles the likelihood of developing nuclear sclerotic cataracts and triples the risk of posterior subcapsular cataracts. Chronic alcohol use can also contribute to the early formation of cataracts, along with other lifestyle factors.
6. Medication Use
Certain medications, especially corticosteroids (used in treating conditions like asthma and inflammation), are known to increase the risk of cataract development. Long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to posterior subcapsular cataracts. Additionally, miotics and triparanol have also been linked to cataract formation.
7. Diabetes
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing cataracts, particularly diabetic cataracts. High blood sugar levels can cause changes in the lens, leading to clouding. This is further compounded by poor diabetes management, which can exacerbate the condition.
8. Vitamin Deficiency
Inadequate vitamin C intake has been associated with an increased risk of cataracts. Low vitamin C levels can impair the eye’s ability to combat oxidative damage, increasing the likelihood of lens clouding.
9. Post-Surgical and Post-Trauma Complications
Following eye surgery, particularly vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous gel), many patients experience nuclear sclerosis, a form of cataract. This is often due to differences between the natural vitreous humor and the vitreous substitutes used during surgery, which lack protective components like ascorbic acid that help protect the lens from oxidative damage.
10. Long-Term Exposure to Glucocorticoids
Prolonged use of glucocorticoid medications, commonly used to treat inflammatory conditions, can induce cataracts. This type of cataract typically develops at the posterior subcapsular location of the lens, which is highly characteristic of glucocorticoid-induced cataracts.
Understanding the different causes of cataracts can help individuals take preventive steps, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying conditions like diabetes, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and quitting smoking.