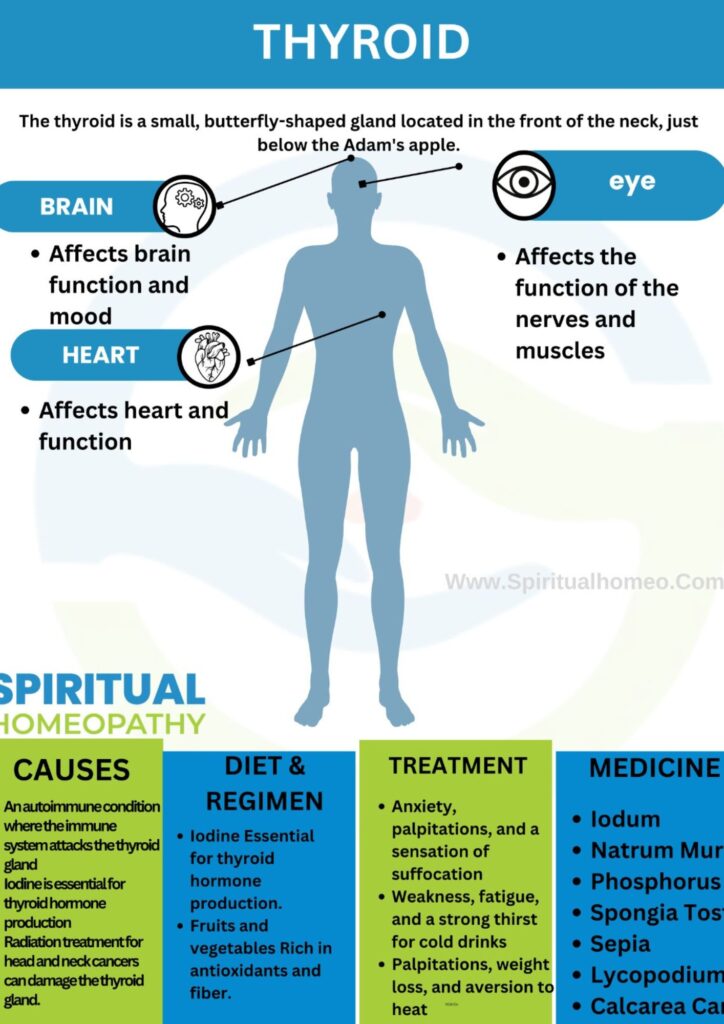
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, just beneath the Adam’s apple. It plays a vital role in controlling the body’s metabolism by producing essential hormones that regulate energy levels, growth, and overall health.
Thyroid
Thyroid Disorders Explained: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
- Home
- Thyroid
Everything You Need to Know
Overview
The thyroid gland, located at the front of the neck below the Adam’s apple, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development by producing thyroid hormones (T4 and T3). These hormones influence many bodily functions, including energy levels, heart rate, and temperature regulation. Disorders of the thyroid, such as hyperthyroidism (overproduction of hormones) and hypothyroidism (underproduction of hormones), can significantly affect overall health and may lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight changes, mood fluctuations, and altered metabolic activity.
Evaluation and management of thyroid-related concerns require proper clinical assessment. Consultations for thyroid disorders are available at Spiritual Homeopathy Clinic across multiple branches in Hyderabad, as well as through online and international consultation options for patient convenience.
Causes of Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis:
An autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production.Iodine Deficiency:
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis. A deficiency may result in decreased thyroid function and hypothyroidism.Thyroid Surgery:
Partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland can lead to hypothyroidism due to reduced hormone production capacity.Radiation Therapy:
Radiation treatment to the head or neck region may damage thyroid tissue, affecting hormone production.Certain Medications:
Some medications can interfere with thyroid hormone production and contribute to hypothyroidism..
Causes of Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Graves’ Disease:
An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system stimulates the thyroid to produce excessive hormones.Thyroiditis:
Inflammation of the thyroid gland that may cause a temporary increase in hormone release. This can be associated with autoimmune conditions, infections, or postpartum changes .
Causes of Goiter (Enlarged Thyroid)
Iodine Deficiency:
Insufficient iodine intake can cause the thyroid gland to enlarge as it attempts to compensate for reduced hormone production, resulting in goiter formation.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
A condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), leading to slowed metabolic activity and symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and low mood.
Causes:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Iodine deficiency
Thyroid surgery
Radiation therapy
Certain medications that affect thyroid function
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Occurs when the thyroid gland produces excess thyroid hormones, resulting in increased metabolic activity. Common symptoms include weight loss, palpitations, heat intolerance, and anxiety.
Causes:
Graves’ disease
Thyroiditis (including postpartum thyroiditis)
Thyroid nodules
Goiter
A visible enlargement of the thyroid gland, often related to iodine deficiency or underlying thyroid dysfunction. Goiters may be associated with either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Causes:
Iodine deficiency
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Graves’ disease
Thyroid Nodules
Solid or fluid-filled lumps within the thyroid gland. Most nodules are benign, though some may affect hormone production or require further evaluation.
Causes:
Benign growths
Thyroid cancer (in rare cases)
Thyroid Cancer
A relatively uncommon condition where malignant cells develop in the thyroid gland. Early evaluation supports timely management and monitoring.
Types:
Papillary thyroid cancer
Follicular thyroid cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (rare and aggressive)
Thyroiditis
Inflammation of the thyroid gland that may cause temporary hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, or both. Neck discomfort or swelling may be present.
Types:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune)
Subacute thyroiditis (often post-viral)
Postpartum thyroiditis
Congenital Hypothyroidism
A condition present at birth in which the thyroid gland is underactive. Early detection is important to support normal growth and development.
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders can lead to a range of symptoms, depending on whether the thyroid is underactive (hypothyroidism), overactive (hyperthyroidism), or affected by conditions such as thyroiditis, goiter, or thyroid nodules. Below are common symptoms associated with various thyroid issues.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid):
Fatigue and sluggishness
Weight gain
Cold intolerance
Dry skin and hair
Constipation
Low mood or depressive symptoms
Memory and concentration difficulties
Muscle weakness and joint pain
Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
Hoarseness of voice
Puffy face
Elevated blood cholesterol levels
Irregular or heavy menstrual periods
The severity and combination of symptoms can vary between individuals and often develop gradually over time. If these symptoms are persistent, progressive, or affecting daily activities, medical consultation is advised for proper evaluation and guidance.
Diet and Regimen for Thyroid Health
Maintaining a healthy diet and daily regimen is essential for supporting thyroid function, whether you have hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). A balanced diet and lifestyle measures can help manage symptoms, support overall thyroid health, and complement ongoing care.
Diet for Thyroid Health
1. Iodine-Rich Foods
Iodine is important for thyroid hormone production. Including iodine-rich foods may support thyroid function, particularly in individuals with dietary deficiency.
Seaweed (kelp, nori, etc.)
Fish (salmon, tuna, cod)
Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
Eggs
Iodized salt
2. Selenium-Rich Foods
Selenium supports thyroid hormone metabolism and helps protect thyroid tissue.
Brazil nuts
Sunflower seeds
Fish (tuna, sardines, salmon)
Eggs
Whole grains (brown rice, barley)
3. Zinc-Rich Foods
Zinc contributes to thyroid function and immune support.
Pumpkin seeds
Shellfish (oysters, crab)
Red meat
Poultry
Legumes (chickpeas, lentils)
4. Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Antioxidants help reduce inflammation and support overall well-being.
Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
Tomatoes
Carrots
Nuts and seeds
5. Healthy Fats
Healthy fats support hormone balance and may help reduce inflammation.
Avocados
Olive oil
Coconut oil
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
6. Vitamin D
Vitamin D supports immune health and may be relevant in autoimmune thyroid conditions.
Fatty fish (salmon, sardines)
Egg yolks
Fortified foods
Safe sunlight exposure
Foods to Limit or Avoid:
Goitrogens (in excess): Present in some cruciferous vegetables and soy products; cooking can reduce their effect.
Processed foods: Often high in sodium and unhealthy fats.
Excess caffeine and alcohol: May interfere with hormonal balance.
Regimen for Thyroid Health
1. Consistent Medical Guidance
Individuals with thyroid disorders should follow medical advice and attend regular reviews to ensure appropriate monitoring and adjustment of care.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps manage weight, supports metabolism, and improves mood.
Moderate activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are commonly well tolerated.
Strength and cardiovascular exercises can be included as appropriate.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress may influence thyroid function. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or time outdoors can be supportive.
4. Adequate Sleep
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep to support hormonal balance and recovery.
5. Regular Checkups
Periodic evaluations and laboratory assessments help monitor thyroid function and overall health.
6. Hydration
Adequate fluid intake supports digestion and skin health and may help ease symptoms such as constipation or dryness.
Yoga Asanas for Thyroid Health
Yoga can be beneficial as a supportive practice for individuals managing thyroid disorders. It may help reduce stress, encourage relaxation, and support overall well-being. Certain yoga poses can gently stimulate the neck region and promote circulation, which may be supportive for thyroid health when practiced correctly and consistently. The following yoga asanas are commonly recommended as part of a balanced lifestyle.
1. Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand)
Benefits:
Helps apply gentle pressure to the neck region and may support circulation around the thyroid area. It is commonly practiced to support hormonal balance and overall vitality.
How to do it:
Lie on your back and lift your legs to a 90-degree angle.
Slowly raise your hips and legs, supporting your lower back with your hands.
Keep the body aligned, with elbows and arms providing support.
Hold for 20–30 seconds, then release slowly.
2. Halasana (Plow Pose)
Benefits:
Provides a stretch to the neck, throat, and shoulders, which may help support thyroid function and relieve muscular tension.
How to do it:
Lie on your back with legs extended and arms at your sides.
Lift your legs over your head, aiming to touch the floor with your feet if comfortable.
Support your lower back with your hands.
Hold for 20–30 seconds, then release gently.
3. Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
Benefits:
Opens the chest and stretches the neck and throat area, supporting flexibility and relaxation.
How to do it:
Lie on your back with legs extended.
Press elbows into the floor and lift your chest upward.
Gently arch your back, allowing the crown of the head to rest lightly on the floor.
Hold for 20–30 seconds, then release.
4. Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose)
Benefits:
A gentle backbend that supports spinal flexibility and circulation near the neck and chest region.
How to do it:
Lie on your stomach with hands under shoulders.
Press into the floor and lift your chest, keeping elbows slightly bent.
Hold for 15–20 seconds, then release slowly.
5. Uttanasana (Standing Forward Bend)
Benefits:
Encourages relaxation of the nervous system and may help reduce stress-related strain.
How to do it:
Stand with feet hip-width apart.
Fold forward from the hips, allowing the head and neck to relax.
Keep knees slightly bent if needed.
Hold for 20–30 seconds, then return slowly.
6. Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
Benefits:
Stretches the neck, chest, and spine and may support circulation in the thyroid region.
How to do it:
Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
Press feet into the ground and lift hips upward.
Hold for 20–30 seconds, then release gently.
7. Kapalbhati (Breath Practice)
Benefits:
A breathing practice that supports digestion, metabolic activity, and overall vitality when done under guidance.
How to do it:
Sit comfortably with the spine straight.
Perform gentle, rhythmic exhalations through the nose while engaging the abdomen.
Practice for 1–3 minutes as tolerated.
8. Trikonasana (Triangle Pose)
Benefits:
Promotes stretching of the neck and spine and supports balance and relaxation.
How to do it:
Stand with legs wide apart and arms extended.
Turn one foot outward and bend sideways, bringing one hand toward the leg.
Keep the neck comfortable and relaxed.
Hold for 20–30 seconds on each side.
🌿 Why Choose Homeopathy?
Homeopathy is a gentle, natural system of healing that focuses on addressing the root cause of illness rather than only the symptoms. It works in harmony with the body’s innate ability to maintain balance and supports overall wellness. Homeopathy is suitable for all ages and is tailored to each individual, offering a holistic approach that can complement long-term health management.
Whether you’re managing a chronic condition or seeking relief from acute symptoms, homeopathy provides a personalized path to support your well-being. Consultations are available at our Hyderabad branches—including Kukatpally, Chandanagar, Dilsukhnagar, and Nallagandla—as well as online and international consultations.
🌟 Spiritual Homeopathy: Supporting Your Natural Health
At Spiritual Homeopathy Clinic, we aim to help you achieve overall wellness—physically, emotionally, and spiritually. Our approach emphasizes identifying and addressing underlying imbalances that contribute to illness, rather than focusing solely on symptoms.
We provide individualized care using classical homeopathy principles, adapted to modern clinical understanding.
💫 Key Features of Our Care
Root-Cause Focus: We go beyond surface symptoms to support deeper, long-term wellness.
Personalized Treatment: Every plan is customized based on your body, lifestyle, and emotional health.
Experienced Team: Our qualified homeopathy doctors in Hyderabad provide in-clinic, online, and international consultations.
Safe & Gentle: Treatments are non-toxic, non-addictive, and generally well-tolerated under professional guidance.
Holistic Approach: Mind-body-spirit connections are considered in every treatment plan.
🔍 Our Treatment Process
🩺 1. Comprehensive Consultation
We take the time to understand your health history, lifestyle, emotional state, and current symptoms to develop an individualized treatment plan.
💊 2. Holistic Remedies
Homeopathic remedies are selected to support your specific condition—whether acute or chronic—while addressing contributing factors in a safe and gentle manner.
🔄 3. Continuous Support & Follow-Up
Regular follow-ups allow us to monitor progress, make adjustments, and provide guidance to support long-term health.
❤️ Our Commitment
At Spiritual Homeopathy Clinic, your health and well-being are our priority. Our team provides attentive, professional care to support recovery, symptom management, and overall vitality.
When to Consult
You should consult a healthcare professional if thyroid-related symptoms become noticeable, persistent, or begin to affect daily activities, energy levels, weight, or emotional well-being. Early evaluation helps identify thyroid imbalance and supports timely, appropriate care.
Seek consultation if you experience:
Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
Persistent fatigue, weakness, or low energy levels
Sensitivity to cold or heat
Hair fall, dry skin, or brittle nails
Irregular menstrual cycles or fertility concerns
Mood changes such as anxiety, irritability, or low mood
Swelling in the neck or a visible lump (goiter)
Changes in heart rate, such as palpitations or slow heartbeat
Symptoms not improving with lifestyle or dietary measures
Prompt medical evaluation is advised if symptoms worsen, interfere with daily life, or are associated with significant physical or emotional changes.
At Spiritual Homeopathy Clinic, consultations are available at multiple branches in Hyderabad, including Kukatpally, Chandanagar, Dilsukhnagar, and Nallagandla. Online and international consultations are also available for individuals who cannot visit in person. A professional assessment supports an individualized care approach based on symptoms, test findings, and overall health status.
For appointments or guidance, contact 9069 176 176.
FAQ – Thyroid Disorders
What is the thyroid gland and what does it do?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck. It produces hormones (T4 and T3) that regulate metabolism, energy, and the functioning of many organs in the body.What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)?
Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin and hair, constipation, depression, muscle weakness, hoarseness, and elevated cholesterol levels.What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)?
Symptoms may include weight loss despite increased appetite, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, tremors, excessive sweating, heat intolerance, insomnia, and frequent bowel movements.How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
Diagnosis is usually through blood tests measuring thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4). High TSH and low T4 levels typically indicate hypothyroidism.What causes hypothyroidism?
Common causes include autoimmune disorders (e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), iodine deficiency, thyroid surgery, radiation therapy, and certain medications.Can diet affect thyroid function?
Yes. Nutrients such as iodine, selenium, zinc, and vitamin D support thyroid health. Deficiencies in these can affect thyroid hormone production.How is hyperthyroidism treated?
Management may include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.Can thyroid disorders cause hair loss?
Yes, both hypo- and hyperthyroidism can lead to hair thinning or hair loss, often noticeable as one of the early symptoms.Are thyroid problems hereditary?
Yes. A family history of thyroid disorders increases the risk of developing thyroid problems.What is the treatment for thyroid disorders?
Treatment depends on the type of disorder. Hypothyroidism is usually managed with hormone replacement, while hyperthyroidism may require medications, radioactive iodine, or surgery. Homeopathic management focuses on individualized care and symptom support under professional guidance.Can yoga help with thyroid health?
Yes. Certain yoga asanas (e.g., Sarvangasana, Bhujangasana, Matsyasana) may help stimulate the thyroid gland, improve circulation, reduce stress, and support hormone balance.How does stress affect thyroid health?
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels, potentially worsening symptoms of both hypo- and hyperthyroidism. Stress management may support overall thyroid function.Can pregnancy affect thyroid function?
Yes. Thyroid function can change during and after pregnancy (e.g., postpartum thyroiditis). Monitoring thyroid levels is important for both maternal and fetal health.What is a goiter?
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, often caused by iodine deficiency or autoimmune conditions, leading to visible neck swelling.How often should I get tested for thyroid function?
People with thyroid disorders should follow their doctor’s recommendations for regular testing. At-risk individuals may consider testing every 1–2 years or more frequently if advised.Is there a connection between thyroid problems and weight changes?
Yes. Hypothyroidism can slow metabolism and cause weight gain, while hyperthyroidism may accelerate metabolism, leading to weight loss.Can thyroid disease be managed effectively?
While thyroid disorders may not always be fully “cured,” they can be managed through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring. Individualized care can support long-term wellness.Can thyroid conditions affect mood?
Yes. Hypothyroidism can cause depression, irritability, and low energy, while hyperthyroidism may lead to anxiety and nervousness.Are there foods to avoid with thyroid disorders?
Limit excessive raw cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cabbage) if you have iodine deficiency. Also, moderate soy intake and highly processed foods, which may interfere with thyroid function.
